Residents Parking
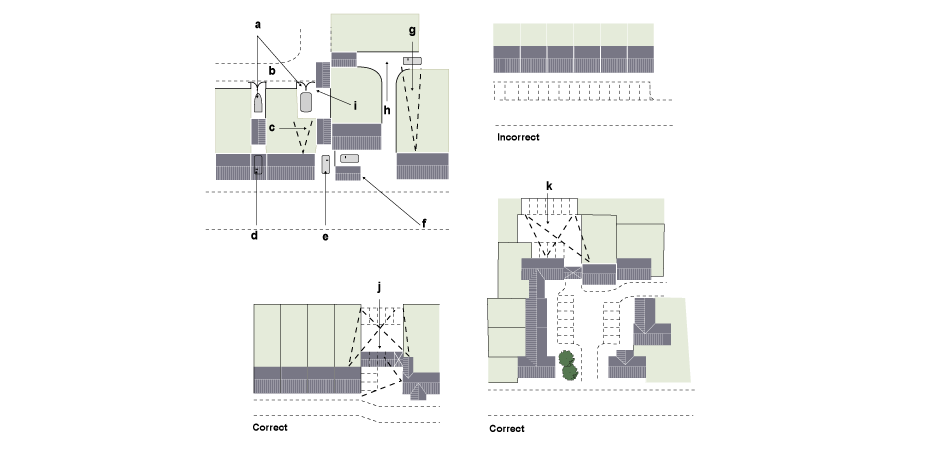
Residents’ spaces or garages may be located on or near the frontage, but in such a way as not to dominate the street scene – for example, through a carriage arch under the building, placed sideways-on to the frontage or down a side-way between houses. Residents’ spaces may also be located at the rear of houses, approached between the houses or from a separate road or drive. In the latter case, care should be taken that the parking space is overlooked from the dwelling served, or else is located within a secure garage so as not to provide an opportunity for theft.
One advantage of rear access to individual plots is the possibility of on-plot parking for caravans and boat trailers.
Communal parking areas should ideally be located so as not to be unduly conspicuous in the layout. In other words, a continuous row of parked cars in front of a terrace of houses is unacceptable. Instead, communal parking areas should be divided and distributed around the layout, with some spaces convenient for visitors on or near the frontage, and others at the side or rear of dwellings. Again, in all cases care should be taken that communal parking areas are overlooked by the kitchen or living-room windows of at least some dwellings, or else by footways in regular use, in order to discourage car-related crime.
Parking Space
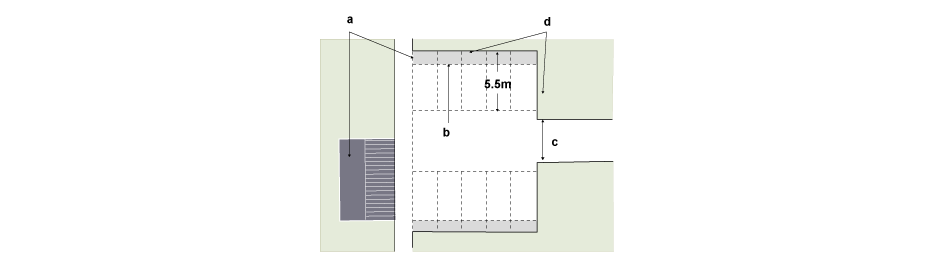
The preferred size of a parking space is 5.5m x 2.9m. When the parking space is located in front of a garage, the long dimension should be 6m so as to allow space to open the garage door. A vehicle and pedestrian sight-splay of 1.5m x 1.5m will typically be required so as to give clear visibility above a height of 600mm where the parking space abuts the rear edge of the footway. Exceptions to this requirement include garages and parking spaces off type F and G roads, parking squares and private drives.
Parking spaces between structures may require an increased area for pedestrian movement around the vehicle. The length and width will relate to the internal dimensions of garages, currently 7m x 3m. In the case of layby parking on a highway, spaces should be 6m x 2m where adjoining a footway or 6m x 2.4m where no footway is provided.

Alternative ways of accommodating parking spaces between or within buildings facing Road Types C-E
a. Splays cut out from building
b. Widen space
c. Set building back from footway
d. Footway
e. Bollards
f. 1.5m x 1.5m sight-splay
A parking space capable of use by disabled people must be widened to 3.6m or adjacent to an area on the same level, such as a lowered footway, containing at least a 1.2.m-wide space for getting in and out of vehicles.
Garages
The minimum internal garage size is 7m x 3m. Where a garage door abuts the back edge of a footway or shared-surface road, the garage should be set back sufficiently for the swept path of the door not to obstruct circulation. However, it should not be set back more than 0.5m unless a full 6m parking space is provided in front. The use of through garages, with doors front and back, is useful in giving access to the rear curtilage for additional parking and storage.
Communal Parking Courts
Parking spaces should be at least 5.5m x 2.9m, and rows should be separated by at least 6m to allow manoeuvring in and out. It may be desirable for some spaces to be designed to accommodate caravans or boats. At least 5% of spaces (with an absolute minimum of one space) in each parking court should be suitable for use by disabled people (see the ‘Parking Space’ section of this guide).
Entrance ways to parking courts should adhere to the following criteria:
- Up to 8 parking spaces – as for shared private drives.
- Nine parking spaces and over – access to be 4.1m in width, centreline bend radius 6m minimum, sight-lines as for private drives, headroom 2.5m. If access for fire tenders is required, refer to the ‘Access for Fire Tenders’ section of this guide.
Apart from small groups of visitor parking spaces on or near the frontage, parking courts should be well-enclosed by buildings or walls to reduce their intrusiveness. At the same time, they should be overlooked by at least some dwellings or footways in regular use, in order to discourage car-related crime. The incorporation of tree and shrub planting will soften the appearance and reduce the apparent size of parking courts, as will the use of more attractive surface materials, such as tar spray and pea shingle dressing, concrete or clay block paving, granite or concrete setts, stable blocks and cobbled edges.
Fences should not be used to enclose parking courts as they are vulnerable to vehicle impact. Walls should be used, and where used at the ends of parking spaces should be protected by a kerb set 600mm into the parking space.
Communal parking court
a. Overlooked by footway and/or dwelling
b. Kerb set 600mm into parking space
c. Appropriate-width entrance way
d. Above eye-level walls
Garage Courts
A minimum width of 7.3m is required between the fronts of garages. The end wall or kerb of a garage court should be recessed so that most types of car are able to manoeuvre. Sufficient space and gullies should be provided for car-washing. Entrance ways should follow the same criteria outlined for parking courts, but headroom may reduce to 2.1m provided fire tender access is not required.
Page updated: 19/02/2018