Building Typologies 3. New build education (schools)
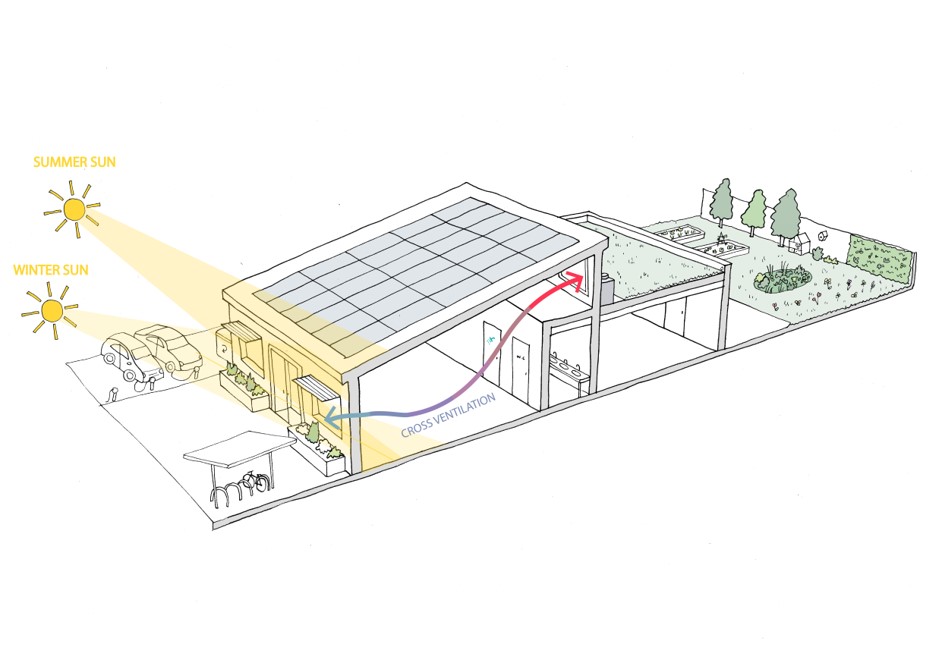
Orientation, overshadowing, daylight and solar gain
- Orientate buildings 30 degrees from South (where possible)
- Place higher elements to the North of the site
- Allow a distance of 1-1.5 times the building’s height between buildings
- Design green amenity space to receive sunlight as per BRE guidance
- Position occupied spaces on the South façade
Glazing
- Favour horizontal windows over vertical glazing
- Use a g-value of between 0.4 - 0.5
- Use LETI glazing ratios: north = 15-25%, east = 15-25%,
south = 15-25%, west = 15-25%
Shading
- South Elevations – use horizontal brise soleil and projecting balconies
- East / West Elevations – Use shutters or external roller blinds
Ventilation
- Design for cross ventilation where possible
- Incorporate blue green spaces into masterplan
Maximise PV
- Maximise renewables so that 70% of the roof is covered
- Mono pitched roofs angled South are able to generate more PV energy than flat roofs
- For flat rooves, design for East West concertina PV array as a opposed to North South
- For mono pitched roofs, slope roof to face South
Opportunities and Constraints
- Often on large open sites, there is an opportunity to maximise the buildings orientation, overshadowing, density and massing.
- Schools often have large areas of roof space, so good potential for PVs, Net Zero Carbon (more energy generated than used on site) is usually achievable and in many cases it is possible to generate more energy which can be exported to the national grid.
- Where possible, schools should aim to be solely naturally ventilated in summer.
Page updated: 27/09/2022